Life Cycle of Plasmo CSUI
Plasmo's CSUI orchestrates a lifecycle dedicated to mounting and unmounting your React, Vue, or Svelte components in a content script. Although each UI library/framework has a slightly different mounting API, the top-level lifecycle is largely the same:
- Get an
Anchor - Create or locate a
Root Container - Render the component onto the
Root Container
Terminologies
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Anchor | Tell CSUI how and where to mount your component |
| Anchor-getter | Tell CSUI how to find your anchor(s) |
| Overlay | Mount your component on a top-level (max z-index) overlay element |
| Inline | Mount your component into the webpage's DOM, next to a target element |
| Root Container | A ShadowDOM element created by CSUI to isolate your component |
| Renderer | The top-level life-cycle runner (it does everything) |
Anchor
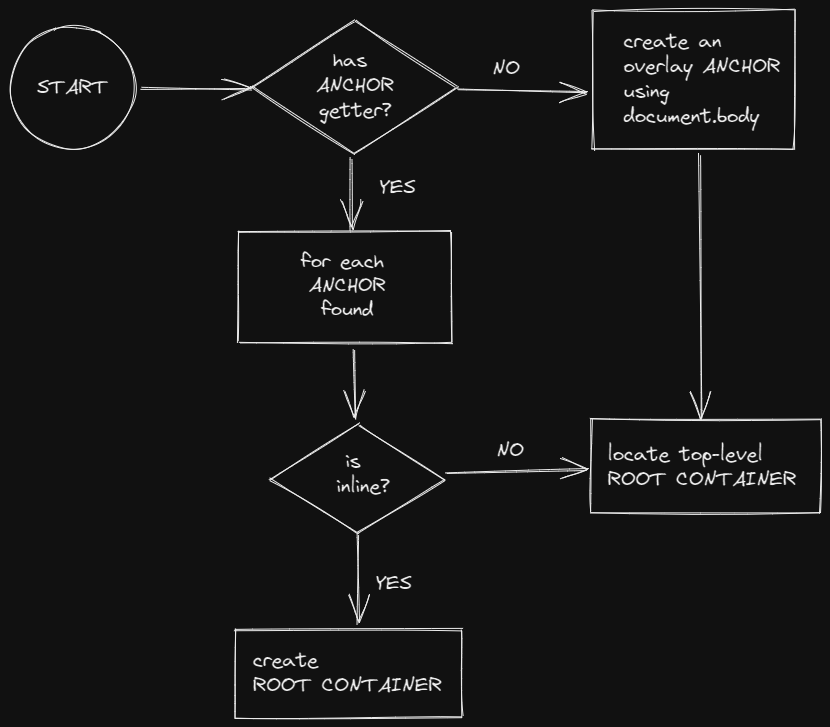
A Plasmo CSUI anchor is defined by the following type:
export type PlasmoCSUIAnchor = {
type: "overlay" | "inline"
element: Element
}By default, the CSUI lifecycle creates an overlay anchor using the document.body element:
{
type: "overlay",
element: document.body
}If any anchor-getter function is defined and exported, the CSUI lifecycle will use the returned element and the relevant anchor type instead. Since the anchor-getter functions can be async, you also have the power to control when Plasmo mounts your component. For example, you can wait for a specific element to appear on the page before mounting your component.
The anchor is passed down to the CSUI via the anchor props. You can access it as follow:
import type { PlasmoCSUIProps } from "plasmo"
const AnchorTypePrinter: FC<PlasmoCSUIProps> = ({ anchor }) => {
return <span>{anchor.type}</span>
}
export default AnchorTypePrinterOverlay
Overlay anchors spawn CSUI Overlay Containers which are batch-mounted onto a single Root Container element per CSUI. The Overlay Containers are absolutely positioned relative to each anchor's element with maxed out z-index. Then, your exported CSUI Component is mounted onto each Overlay Container:
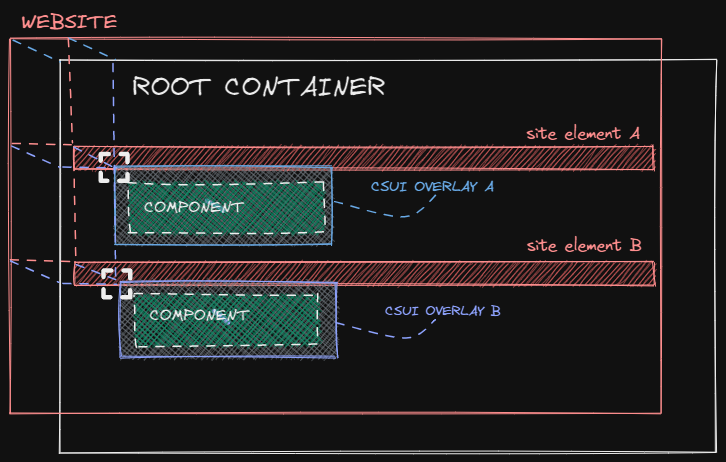
To specify a single overlay anchor, export a getOverlayAnchor function:
import type { PlasmoGetOverlayAnchor } from "plasmo"
export const getOverlayAnchor: PlasmoGetOverlayAnchor = async () =>
document.querySelector("#pricing")To specify a list of overlay anchors, export a getOverlayAnchorList function:
import type { PlasmoGetOverlayAnchorList } from "plasmo"
export const getOverlayAnchorList: PlasmoGetOverlayAnchorList = async () =>
document.querySelectorAll("a")getOverlayAnchorList does not cover dynamic case at the moment. For example,
if new anchors are added to the web page after the initial rendering, the CSUI
lifecycle will not be able to detect it. PR is welcome to improve this
feature!
Update Position
The default Overlay Container listens to the window scroll event to align itself with the anchor element. You can customize how the Overlay Container refreshes its absolute positioning by exporting a watchOverlayAnchor function. The example below refreshes the position every 8472ms:
import type { PlasmoWatchOverlayAnchor } from "plasmo"
export const watchOverlayAnchor: PlasmoWatchOverlayAnchor = (
updatePosition
) => {
const interval = setInterval(() => {
updatePosition()
}, 8472)
// Clear the interval when unmounted
return () => {
clearInterval(interval)
}
}Check with-content-scripts-ui/contents/plasmo-overlay-watch.tsx (opens in a new tab) for an example.
Inline
Inline anchor embeds your CSUI Component directly into the web page. Each anchor spawns a Root Container appended next to its target element. Within each Root Container, an Inline Container is created which is then used to mount the exported CSUI Component:
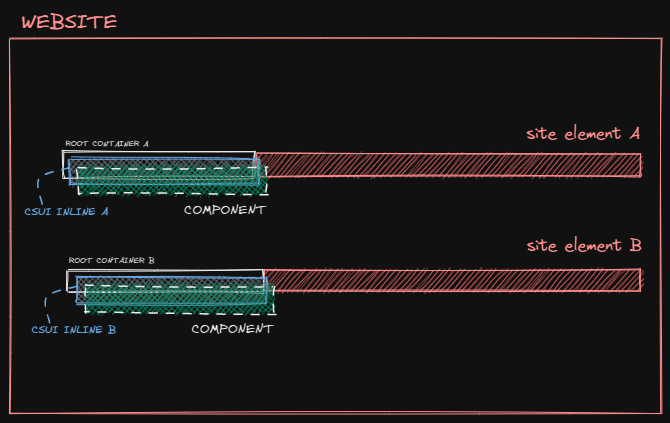
To specify a single inline anchor, export a getInlineAnchor function:
import type { PlasmoGetInlineAnchor } from "plasmo"
export const getInlineAnchor: PlasmoGetInlineAnchor = async () =>
document.querySelector("#pricing")To specify single inline anchor with insert position:
import type { PlasmoGetInlineAnchor } from "plasmo"
export const getInlineAnchor: PlasmoGetInlineAnchor = async () => ({
element: document.querySelector("#pricing"),
insertPosition: "afterend"
})To specify a list of inline anchors, export a getInlineAnchorList function:
import type { PlasmoGetInlineAnchorList } from "plasmo"
export const getInlineAnchorList: PlasmoGetInlineAnchorList = async () =>
document.querySelectorAll("a")To specify a list of inline anchors with insert position:
import type { PlasmoGetInlineAnchorList } from "plasmo"
export const getInlineAnchorList: PlasmoGetInlineAnchorList = async () => {
const anchors = document.querySelectorAll("a")
return Array.from(anchors).map((element) => ({
element,
insertPosition: "afterend"
}))
}Check with-content-scripts-ui/contents/plasmo-inline.tsx (opens in a new tab) for an example.
Root Container
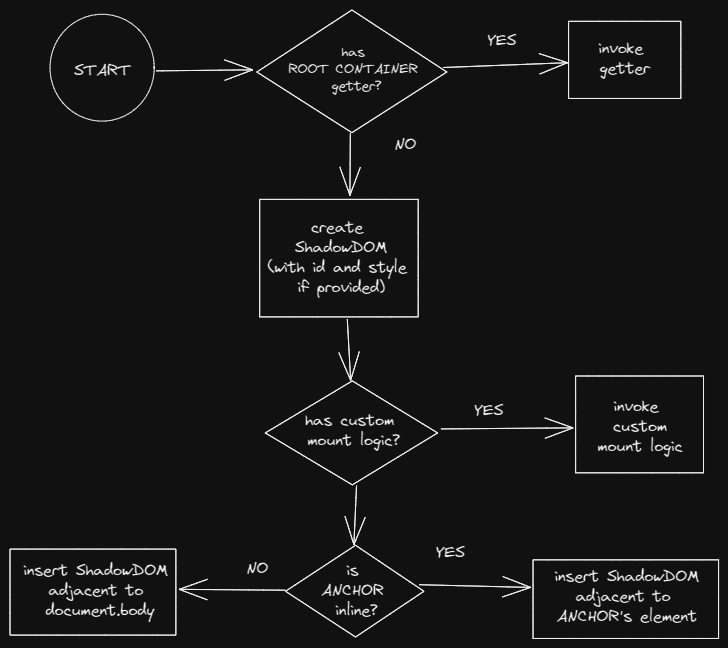
The Root Container is where your CSUI Component is mounted. The built-in Root Container is a ShadowDOM element with the plasmo-csui custom tag. This allows you to style the Root Container and their exported components without being impacted by the web page's styles.
Custom DOM Mounting
The Root Container creates a shadowHost which gets injected into the web page's DOM tree. By default, Plasmo injects the shadowHost after the element for an inline anchor, and before the document.body for an overlay anchor. To customize this behavior, export a mountShadowHost function:
import type { PlasmoMountShadowHost } from "plasmo"
export const mountShadowHost: PlasmoMountShadowHost = ({
shadowHost,
anchor,
mountState
}) => {
anchor.element.appendChild(shadowHost)
mountState.observer.disconnect() // OPTIONAL DEMO: stop the observer as needed
}Closed Shadow Root
By default, the shadow root is "open," allowing anyone (developer and extension user) to inspect the hierarchy of the ShadowDOM. To override this behavior, export a createShadowRoot function:
import type { PlasmoCreateShadowRoot } from "plasmo"
export const createShadowRoot: PlasmoCreateShadowRoot = (shadowHost) =>
shadowHost.attachShadow({ mode: "closed" })Custom Styles
The built-in ShadowDOM provides a convenient mechanism for extension developers to safely style their components by exporting a getStyle function that returns an HTML style element (opens in a new tab).
For further guidance on styling CSUI, please read Styling Plasmo CSUI.
Custom Root Container
Sometimes, you'll want to completely replace Plasmo's Shadow DOM container implementation to fit your needs. For example, you might want to piggyback on an element within the web page itself instead of creating a new DOM element. To do so, export a getRootContainer function:
import type { PlasmoGetRootContainer } from "plasmo"
export const getRootContainer = () => document.getElementById("itero")Some reasons you'd want to do this:
- The extension needs to absorb the styling of the host webpage (opens in a new tab)
- The extension needs to mount the component directly into the webpage instead of using a shadow DOM
- The extension needs to use an iframe (opens in a new tab), instead
If you export a getRootContainer function, any function that extends the
built-in ShadowDOM such as getStyle or getShadowHostId will be ignored.
Call those functions within your custom getRootContainer logic as needed!
Check with-content-scripts-ui (opens in a new tab) for an example.
Renderer
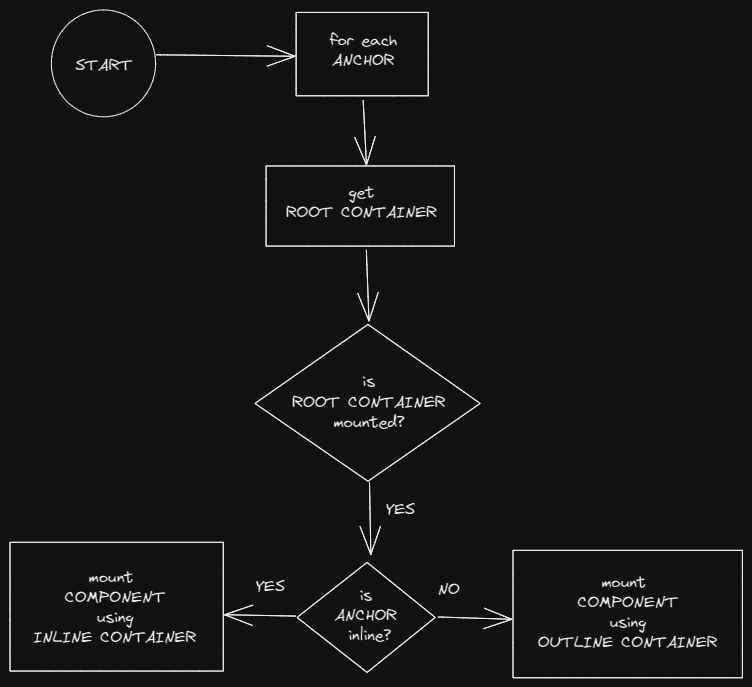
The Renderer is in charge of observing the website's DOM to detect the presence of each Root Container and tracking the linking between each anchor's element and its Root Container. Once a stable Root Container is determined, the Renderer mounts the exported CSUI Component into the Root Container using either an Inline Container or an Overlay Container, depending on the type of the Anchor.
Detecting and Optimizing Root Container Removal
When a webpage changes its DOM structure, the Root Container might be removed. For example, given an email client filled with inbox items, and a CSUI injected inline next to each item. When an item is deleted, the root container will be removed as well.
To detect Root Container removal, the CSUI Renderer compares each mounted container's root against the window.document object. This check can be optimized to O(1) by exporting a getShadowHostId function:
import type { PlasmoGetShadowHostId } from "plasmo"
export const getShadowHostId: PlasmoGetShadowHostId = () => `adonais`The function also allows developers to customize the id for each anchor found:
import type { PlasmoGetShadowHostId } from "plasmo"
export const getShadowHostId: PlasmoGetShadowHostId = ({ element }) =>
element.getAttribute("data-custom-id") + `-pollax-iv`Custom Renderer
Developers may export a render function to override the default renderer. You might need this ability to:
- Provide a custom
Inline containerorOverlay container - Customize the mounting logic
- Provide a custom
MutationObserver
For example, to use an existing element as a custom container:
import type { PlasmoRender } from "plasmo"
import { CustomContainer } from "~components/custom-container"
const EngageOverlay = () => <span>ENGAGE</span>
// This function overrides the default `createRootContainer`
export const getRootContainer = () =>
new Promise((resolve) => {
const checkInterval = setInterval(() => {
const rootContainer = document.getElementById("itero")
if (rootContainer) {
clearInterval(checkInterval)
resolve(rootContainer)
}
}, 137)
})
export const render: PlasmoRender = async ({
anchor, // the observed anchor, OR document.body.
createRootContainer // This creates the default root container
}) => {
const rootContainer = await createRootContainer()
const root = createRoot(rootContainer) // Any root
root.render(
<CustomContainer>
<EngageOverlay />
</CustomContainer>
)
}How to dynamically create a custom container:
import type { PlasmoRender } from "plasmo"
import { CustomContainer } from "~components/custom-container"
const EngageOverlay = () => <span>ENGAGE</span>
// This function overrides the default `createRootContainer`
export const getRootContainer = ({ anchor, mountState }) =>
new Promise((resolve) => {
const checkInterval = setInterval(() => {
let { element, insertPosition } = anchor
if (element) {
const rootContainer = document.createElement("div")
mountState.hostSet.add(rootContainer)
mountState.hostMap.set(rootContainer, anchor)
element.insertAdjacentElement(insertPosition, rootContainer)
clearInterval(checkInterval)
resolve(rootContainer)
}
}, 137)
})
export const render: PlasmoRender = async ({
anchor, // the observed anchor, OR document.body.
createRootContainer // This creates the default root container
}) => {
const rootContainer = await createRootContainer(anchor)
const root = createRoot(rootContainer) // Any root
root.render(
<CustomContainer>
<EngageOverlay />
</CustomContainer>
)
}To utilize the built-in Inline Container or Overlay Container:
import type { PlasmoRender } from "plasmo"
const AnchorOverlay = ({ anchor }) => <span>{anchor.innerText}</span>
export const render: PlasmoRender = async (
{
anchor, // the observed anchor, OR document.body.
createRootContainer // This creates the default root container
},
_,
OverlayCSUIContainer
) => {
const rootContainer = await createRootContainer()
const root = createRoot(rootContainer) // Any root
root.render(
// You must pass down an anchor to mount the default container. Here we pass the default one
<OverlayCSUIContainer anchor={anchor}>
<AnchorOverlay anchor={anchor} />
</OverlayCSUIContainer>
)
}If you need to customize the MutationObserver, do not export an anchor-getter function. Otherwise, the built-in MutationObserver will still be spawned.